Industrial automation technology represents a significant shift in manufacturing paradigms. By incorporating advanced control systems, robotics, and sensors, industries can minimize human input in production processes. This approach enhances efficiency and precision, enabling real-time data processing. As organizations increasingly adopt these technologies, they can streamline operations and reduce costs. However, understanding the underlying components and their implications is essential for grasping the full impact of this transformation on future industrial landscapes.
Understanding the Basics of Industrial Automation
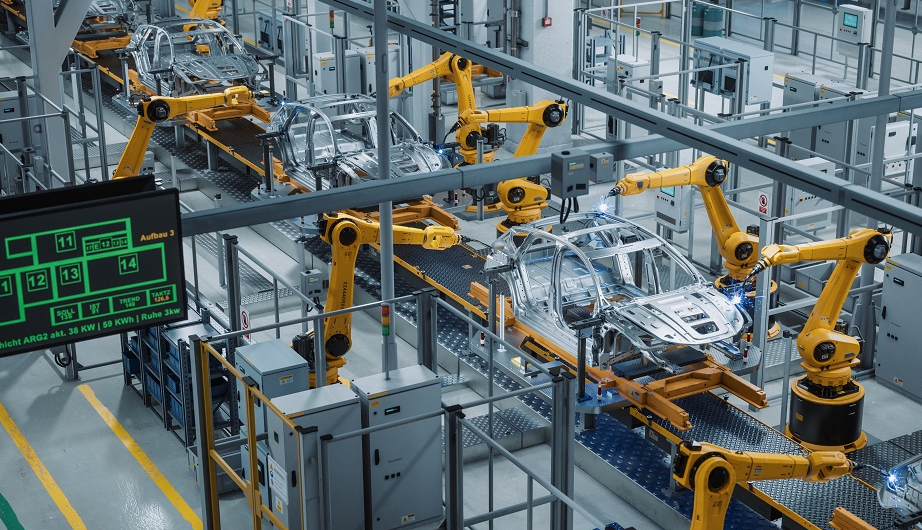
Industrial automation represents a transformative approach in manufacturing and production processes, characterized by the use of control systems such as computers or robots for handling different processes and machinery.
The integration of robotic systems enhances efficiency and precision, allowing for reduced human intervention. This evolution empowers organizations to optimize operations, reduce costs, and maintain flexibility, ultimately fostering an environment conducive to innovation and growth.
See also: Immersive Technology in Professional Industries
Key Technologies Driving Automation
The landscape of automation is significantly shaped by a variety of advanced technologies that enhance operational capabilities.
Key among these are robotic systems and sensor integration, which facilitate real-time data processing and adaptive responses.
Robotic systems streamline tasks, while sensor integration ensures accurate monitoring and control, fostering efficiency and flexibility.
Together, these technologies empower industries to achieve unprecedented levels of productivity and innovation.
Benefits of Implementing Automation in Industries
Implementing automation in industries yields significant advantages that enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Key benefits include substantial cost savings through reduced labor expenses and minimized errors.
Additionally, automation improves workforce efficiency by reallocating human resources to more strategic tasks, thereby driving productivity.
These factors collectively enable companies to optimize their processes, adapt to market changes, and ultimately achieve greater economic sustainability.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation
As industries increasingly recognize the benefits of automation, attention shifts towards emerging trends that will shape the future landscape of this technology.
Robotic advancements are expected to enhance operational efficiency, while predictive maintenance will minimize downtime and reduce costs.
Together, these innovations promise to optimize production processes, enabling companies to respond dynamically to market demands and ensuring greater autonomy in manufacturing environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, industrial automation technology fundamentally transforms manufacturing by enhancing efficiency and precision while reducing operational costs. Although some may argue that automation threatens job security, it is essential to recognize that it also creates opportunities for workforce reskilling and the development of higher-value roles. By reallocating human resources towards innovation and strategic decision-making, industries can leverage automation not merely as a replacement for labor but as a catalyst for economic growth and competitive advantage.